Founded in 1956, the Department of Sediment Research is mainly engaged in the sediment problems in rivers, reservoirs and estuaries, and soil and water conservation. The research fields cover fluvial processes and river training, reservoir sedimentation and its optimum operation, estuary sediment and its training, mechanism and monitoring and restoration of soil erosion, sediment problems in water-related projects. The department has the Key Laboratory of Sediment Science and Northern River Training of the Ministry of Water Resources, and the Research Center of Soil Conservation Ecological Engineering Technology of the Ministry of Water Resources. The Department has 4 large laboratories, with a total construction area of 14,000m2. The department has two 5-star certificates for soil and water conservation program compilation and monitoring and evaluation. It undertakes the daily work of the Sediment Committee of the Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society and the Scientific and Technological Cooperative Working Committee of the Chinese Society of Soil and Water Conservation, as well as the edition and publication of the Journal of Sediment Research.
The Department has 7 research sections and 57 employees, including 33 professor-level senior engineers, 15 senior engineers and 7 engineers. Among them, 49 people hold doctoral degrees and 5 people hold Master's degrees.
Section of River Sediment and Management
· Basic theories of sediment transport and riverbed evolution
· R&D of measurement and metrology techniques for turbulence and sediment transport
· Research on sediment issues in river management and water-related projects
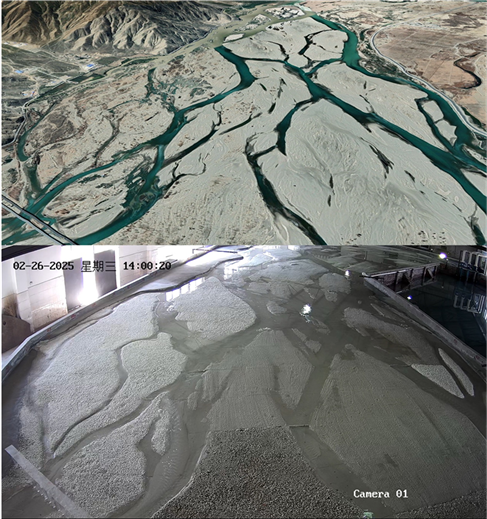

Hydraulic model tests on river evolution, management, and sediment transport

Tomo-PIV measurement system for near-wall turbulence-sediment coupled movement
Section of Reservoir and Lake Sedimentation
· Reservoir sedimentation and optimum operation
· Water intake and sediment control of hydropower stations
· Reservoir sediment discharging and dredging
· Influence of water-sediment regulation on downstream river
· Flood risk in the backwater area of reservoir due to sedimentation
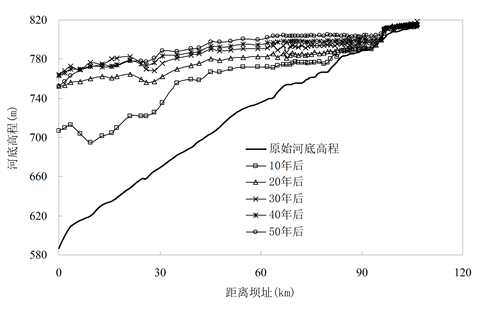
Numerical simulation of sedimentation in the Dongzhuang Reservoir
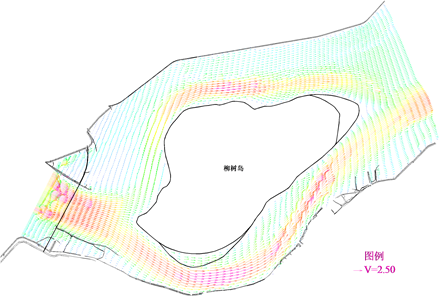
Numerical simulation for flow in the Songhua River

Physical model test for erosion funnel in front of sediment flushing tunnel
Section of Estuary and Coast Sedimentation
· Sediment movement and evolution at estuaries and coasts
· Storm surge forecasting and disaster assessment for estuary and coast
· Estuarine navigation waterway regulation measures
· Sedimentation in the harbor area and area downstream gates and their reduction techniques
· Water intake and sediment prevention for coastal power plants
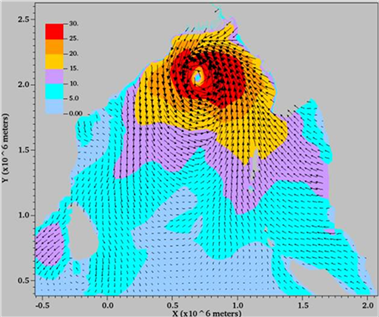
Storm surge forecasting system for the Bengal Bay
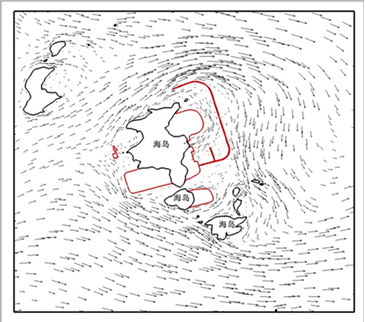
Simulation of flow field around water intake project
Section of Hydro-Sediment Environment Simulation
· Fundamental study on non-uniform and non-equilibrium sediment transport
· R&D of the cross-scale and multi-environmental factors simulation technology
· Development and application of the cross-scale and multi-environmental factors simulation system
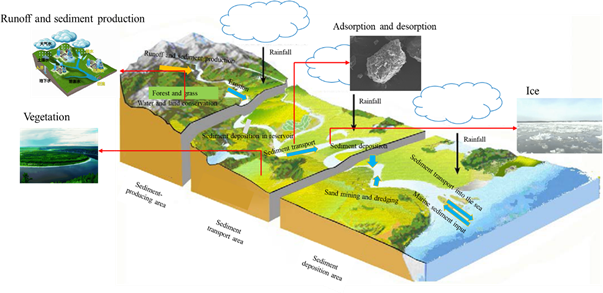
Schematic diagram of sediment-related environment processes

Schematic Diagram of the cross-scale all-dimensional environment simulation system workflow
Section of Soil and Water Conservation Engineering Technology
· Watershed system management and high-quality development
· Watershed water-sediment-carbon processes and multi-objective collaborative regulation
· Soil and water conservation intelligence and remote sensing monitoring
· Mechanism and prevention of human-induced soil erosion
· Ecological value and carbon sink capacity of soil and water conservation
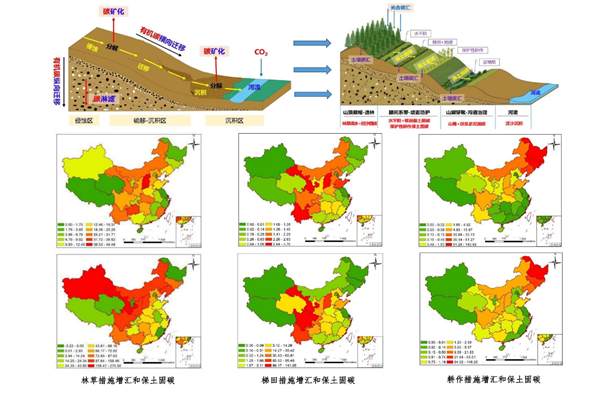
The carbon sink benefits of soil and water conservation measures

Integrated Regulation of Water, Sediment, and Carbon in River Basins
Section of Soil & Water Conservation Monitoring and Evaluation
· Forewarning and forecast of slope and gully erosion
· Efficient vegetation restoration and optimized configuration
· Digital intelligence-based monitoring and evaluation of soil & water conservation
· Mountainous eco-hydrological processes and regulation

Risk forewarning of gully erosion using stacking model of multiple machine learning algorithms in the black soil region of Northeast China
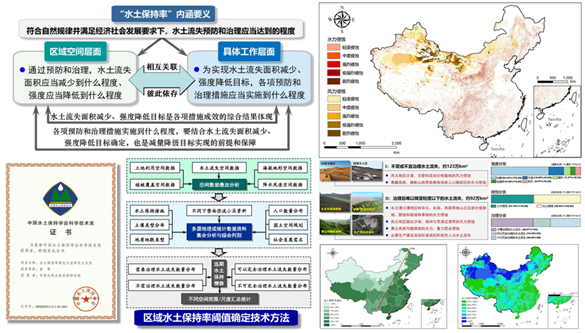
Theory and method of Soil & Water Conservation Rate
Section of Watershed Water and Sediment Processes and Regulation
· Quantitative monitoring of soil and water loss on slopes
· Optimal layout of watershed water and sediment regulation systems
· Modeling of watershed water and sediment dynamic processes
· Response of riverbed variation to watershed water and sediment processes
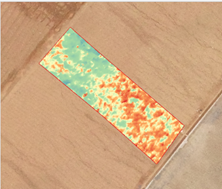

Quantitative analysis of soil loss on artificial slopes
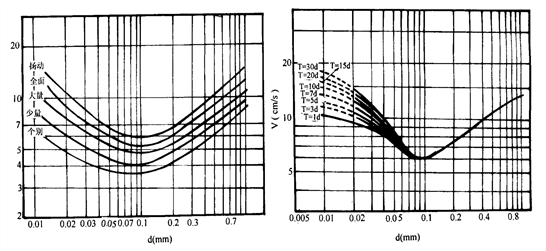
Investigating the velocity of different starting states of granular materials