Main Participants: GAO Bo, LIU Xiaobo, WU Yanhong, LU Jin, WU Wenqiang, BING Haijian, GAO Jijun, WAN Xiaohong, XU Dongyu, NI Jie, NING Zhen, CUI Meng
The Three Gorges Reservoir regulates its storage by adopting an anti-seasonal mode of " store in winter and discharge in summer ", thus generating a water-level fluctuation (WLF) zone with a amplitude up to 30m. The WLF zone experiences frequent exchanges of substances and energy, and also becomes the most sensitive and ecologically vulnerable region in the whole reservoir area. Since the Three Gorges Reservoir starts impounding, heavy metal pollution in the reservoir area has been an issue of international concerns. The unique anti-seasonal mode of the Three Gorges disrupts the natural hydrological rules, inevitably altering the original water and soil environment in the WLF zone. With combined interference and influence from nature and humans, the biogeochemical processes of heavy metals in the WLF zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir becomes even more complex. Therefore, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to research on the biogeochemical processes of heavy metals in the WLF zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir in an anti-seasonal regulation mode.
· Based on the long-sequence field monitoring data, the research has revealed the spatio-temporal evolution patterns of heavy metals in the WLF zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir and their primary driving mechanisms. The research has set out the spatio-temporal distribution patterns of labile heavy metals in the WLF zone and the dynamic mechanisms of water-soil interface release. Through high-resolution mass spectrometry and in-situ monitoring techniques, the research has also uncovered the intrinsic driving mechanisms of DOM in soil of the WLF zone influencing the migration and release of the labile heavy metals at the molecular level;
· Based on the "geochemical baseline model - improved enrichment factor model, labile heavy metals - toxicity data, soil erosion model - rainfall leaching model", the research team has constructed a scientific assessment system for "comprehensive environmental risk - ecotoxicological risk - labile metals inflow flux". It has systematically assessed the comprehensive environmental risk and ecotoxicity risk of heavy metals in the WLF zone, and estimated the inflow and release flux of labile heavy metals in soil of the WLF zone in the reservoir area;
· Combining field research and laboratory simulation, the research team has revealed the migration characteristics and release dynamics of labile heavy metals in soil of the WLF zone with the anti-seasonal storage regulation mode of the Three Gorges Reservoir. It has also investigated the impact mechanism of the anti-seasonal regulation mode on the transformation of valence states of multi-valent heavy metals in the WLF zone, elucidating the migration and transformation patterns of valence states of labile heavy metals in the WLF zone mediated by microorganisms, along with their driving factors.
· The aforementioned theoretical research findings have been published in prestigious SCI journals in the fields of environmental science, hydrology, and water resources, including Water Research, Science of the Total Environment, Journal of Hydrology, Environmental Pollution, and other Chinese core journals in environmental science and lake science.
· The theoretical achievements have been compiled into one monograph, titled "Characteristics and Environmental Effects of Sedimentation of Phosphorus and Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir" (published by Science Press). The monograph received funding support from the National Publishing Fund Project in 2021 and was selected as part of the "13th Five-Year Plan" National Key Publishing Project.
· Two analytical standards have been proposed. The developed in-situ information extraction and risk prediction technology for pollutants in the WLF zone of lakes and reservoirs has been selected into the 2022 Guidance for the Key Promotion of Advanced and Practical Water-related Technology.
The theoretical achievements have gained wide attention from fellows and experts across the world. Nine representative SCI articles have been cited 363 times (47 times per article) by more than 70 international mainstream journals in the fields of environment and ecology, geoscience, hydrology, and water resources, as well as over 130 institutions in more than 30 countries. Among them, the articles have received more than 110 other-citations in zone 1/top-tier journals in the field of environment and ecology, such as Environmental Science & Technology, Water Research, Journal of Hazardous Materials, and Journal of Hydrology. The citations come from over 150 global universities and research institutes including Yale University, Cornell University, University of London, University of Zurich, University of Tokyo, Tsinghua University, Peking University, Beijing Normal University, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences.
Figure 1 Research Roadmap for Biogeochemical Processes of Heavy Metals in Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir
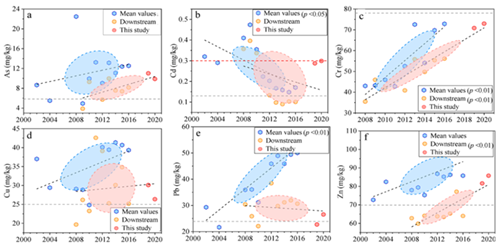
Figure 2 Evolution Characteristics of Total Concentration of Heavy Metals in Soil in Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir
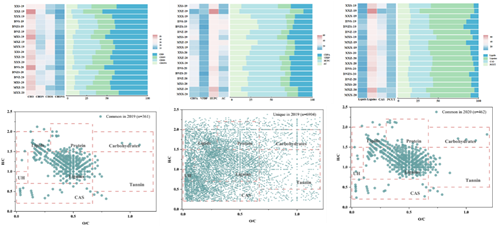
Figure 3 High-resolution Mass Spectrum Characteristics of DOM
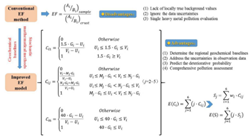

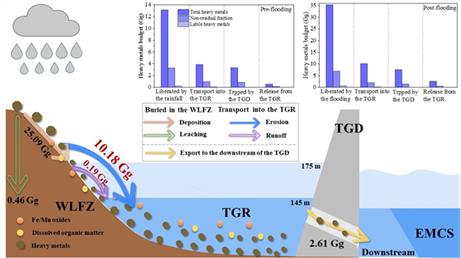
Figure 4 Ecotoxicity Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir and Estimation of Inflow Load of Labile Heavy Metals
Figure 5 Migration and Transformation Mechanism of labile As in Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir under Anti-seasonal Regulation and Storage Mode