Main Participants: Lu Fan, Ruan Benqing, Zhao Yong, Sun Wenchao, Gong Jiaguo, Zhou Yuyan, Tang Yingfu, Cao Jiansheng, Hou Baodeng, Chen Haiyang, Wang Shiqin, Zhang Jinping, Tao Yuan, Dong Ningpeng, Xu Yiran, Song Xinyi, Wu Chu, Yang Hui, Wang Hejia, Jiang Ming
· Carrying out basic research on the ecological and hydrological evolution of the Lake Baiyangdian, the extrapolation of water demand in the Xiong’an New Area, the evolution of runoff in mountainous areas of the Daqing River basin, the optimization of upstream reservoirs operation and their potentials for ecological water replenishment, causes and risks of water pollution in rivers entering the Lake Baiyangdian, and mechanisms on river pollutants migration and conversion;
· Developing automatic monitoring equipment for water amount and quality based on the Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT), building a water quantity-quality-dynamics coupling simulation model covering reservoirs, canals, rivers and lakes; developing a cloud platform for decision-making on comprehensive guarantee of ecological water replenishment and its quality; and developing and demonstrating technologies for restoring and protecting various types of wetlands;
· Propose an overall plan and countermeasures for water security in the Xiong’an New Area.
· Having explained the coupling mechanism of "water cycle, water ecology and water dynamics" in shallow lakes, and extrapolated for the first time the multipurpose water demand integrating “river-lake-city” in the new area based on multiple temporal-spatial scales following the national strategy of high-quality development;
· Having created a multi-factor, whole-process research system for systematically analyzing the mechanism of "source-flow-convergence" evolution and interaction in the water cycle of the fan-shaped river basins, which has provided an important scientific basis for quantitative assessment of the basin-wide risk of water shortage and environmental pollution in channels for ecological water replenishment;
· Having established a complete system of technologies for "real-time sensing, dynamic simulation and optimized decision-making" of the ecological water replenishment process and for wetland habitat restoration, thus improving the monitoring frequency, simulation accuracy and decision-making efficiency, and enhancing the hydrological connectivity, biodiversity and the stability of the species composition;
· Having proposed an integrated plan of "ecological conservation in mountainous areas, water saving and pollution control in plain areas, space optimization in the Lake Baiyangdian and joint allocation of multiple sources and channels", in light of the concept of "combining sources, flow and convergence and coordinating water quantity, quality and aquatic life", reliably supporting the water security in the Xiong’an New Area.
This project have supported the drafting of several key plans such as the Master Plan for the Xiong’an New Area in Hebei Province and the Baiyangdian Eco-environment Management and Protection Plan; also propped up the construction of major projects such as the storage reservoir and main canal in Xiong’an, water purification of the wetlands at the estuary of the Fuhe River and reclaiming farmland to Lake Baiyangdian. The project outcomes have also applied to the governance on ecological water replenishment and groundwater overdraft in Xiong’an, water conservation and water resources allocation, eco-environmental management and ecological conservation in mountainous areas in the Daqing River basin, etc. This project has improved the water security and risk control capability of the Xiong’an New Area, with significant economic, social and ecological benefits and promising future for further promotion and application.

Figure 1 China-UK cooperation on water ecology protection in Lake Baiyangdian
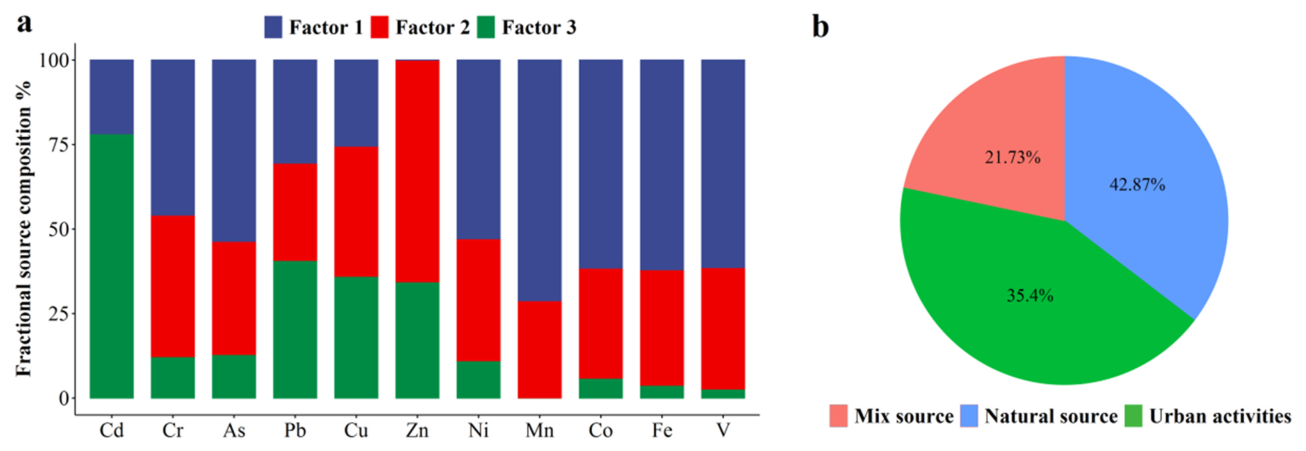
Figure 2 (a) Source profiles of the heavy metals derived from
the PMF model, and (b) the average contribution ratios for the identified
sources. The mix source represents agricultural and industrial activities.
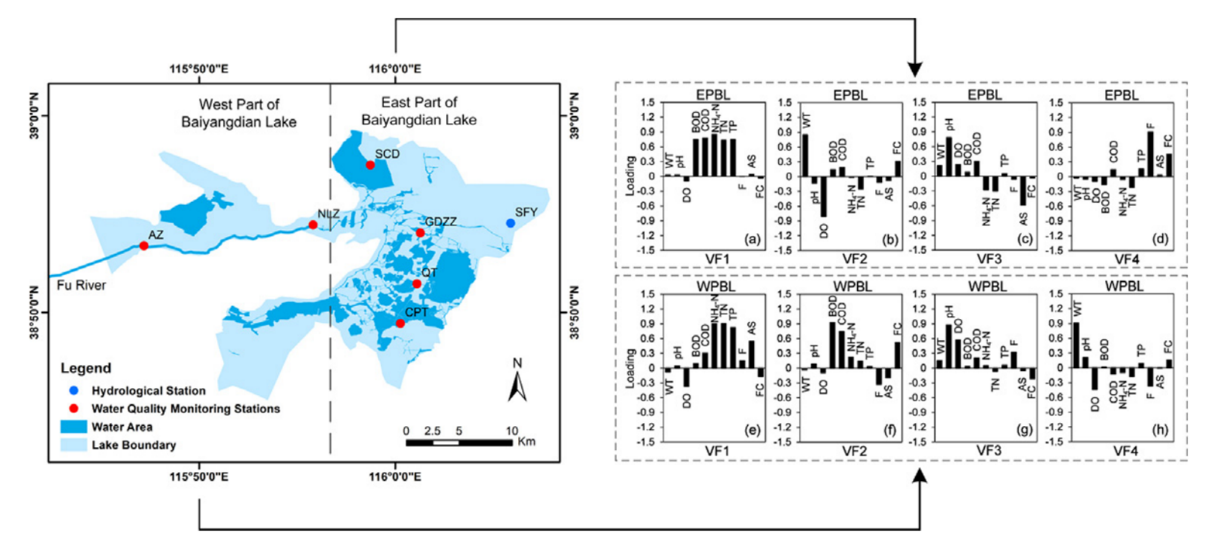
Figure 3 Component loadings of
varifactor (VF) for the water quality data in the stations located in (a–d)
Eastern Part of Baiyangdian Lake (EPBL) and (e–h) Western Part of Baiyangdian Lake (WPBL).

Figure 4 Demonstration projects for automatic monitoring of water amount and quality and wetlands restoration