Main Participants: LIU Jiahong, LI Xiang, ZHAO Yong, SHAO Weiwei, MEI Chao, WANG Jia, GAO Xichao, BI Wuxia, ZHAO Heng, HE Guohua, ZHANG Shanghong, WANG Fuqiang
Water security is a major challenge for regional sustainability in China, especially in a changing environment, where water cycle in city clusters has undergone remarkable changes, giving rise to an urgent need for theoretical and technological support in ensuring regional water security. Located in China’s capital economic circle, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (the BTH region) is a city cluster with the greatest development potential in northern China and one of the regions with the most violent water cycle disturbance in the world. The long-standing contradiction between regional sustainable development and considerably inadequate water resources carrying capacity continues to exacerbate. Sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program, this research explores the theory and technology for analysis of water cycle and diagnosis of water security in city clusters, providing fundamental scientific support for ensuring the security of water resources and managing water risks in city clusters.
· Analyzing the evolution rules of dualistic natural-social water cycle fluxes in city clusters;
· Developing an urban water cycle simulator for building a healthy water cycle pattern;
· Building a dual-source, multi-layer hybrid model for urban water consumption calculation based on urban land use types;
· Studying the driving mechanism and quantification method for the dualistic natural-social water cycle in city clusters;
· Analyzing the water use efficiency based on the spectral discretization method;
· Evaluating the regional water cycle health in city clusters based on the cloud model;
· Mapping the county-level spatial distributions of water resources security in city clusters;
· Monitoring and evaluating the water cycle health of an urban area based on several precipitation events.
· The driving mechanism and quantification method of water cycle in city clusters have been proposed. A dualistic natural-social water cycle flux dataset has been created for the BTH region. The theory of urban water demand field has been established. The coupling characteristics of the natural-social water cycle system have been revealed. A dual-driver mathematical model incorporating both natural and social dimensions has been developed.
· The evolution mechanism of urban water cycle and the high water consumption phenomena have been revealed. An urban water cycle simulator and a model for building a healthy water cycle pattern have been developed. With the proposal of the method of full-caliber calculation of urban water consumption, the deficiencies of existing hydrological models have been made up, such as “ignoring the evapotranspiration from urban anthropogenic water consumption”.
· A method for analysis and spectral discretization of water use efficiency has been developed. Based on the Gamma function discretization and by fitting the spectrum curve of water use efficiency, the feature of “double-peak” during the process of China’s water use efficiency improvement, as well as the imbalance of water use efficiency within the same region have been revealed.
· A multi-scale evaluation model for water cycle health and a method of water security diagnosis have been developed. A method for evaluating regional water cycle health based on the cloud model and a method for evaluating urban water cycle health based on multi-factor monitoring have been developed to assess the water cycle health at city and region levels. A method is proposed for projecting county-level socioeconomic and water demand and diagnosing water security for coordinated development of a city cluster, and the spatial distributions of water security at county-level in city clusters have been mapped.
The research achievements have been fully applied in the BTH region, supporting the assessment of water security and the planning and decision-making of major engineering projects for coordinated regional development, including the determination of the regulation approach of the water cycle in Beijing Municipal Administrative Center and the third evaluation of water resources in the Hai River Basin. The research also provides a scientific basis for enforcing the principle of “Determine the city scale, land use, population growth and industrial development in line with water availability”, with significant socioeconomic and eco-environmental benefits generated.
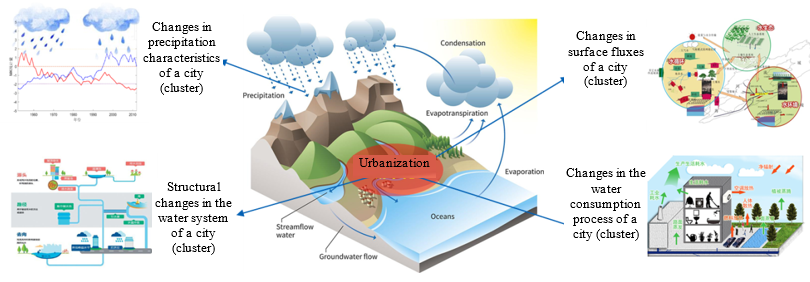
Fig.1 Major Impacts of Urbanization on Natural Water Cycle Process and Regional Water Security
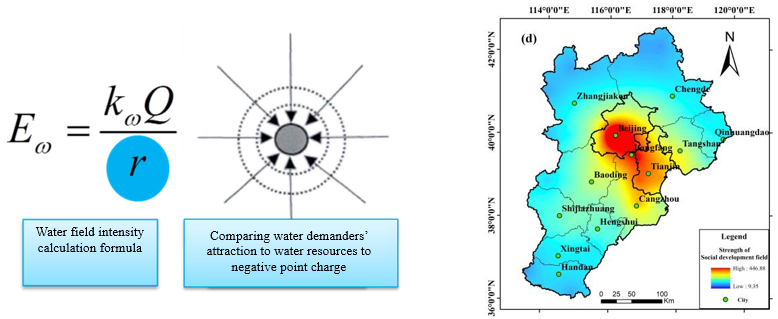
Fig.2 The “Water Field” Theory and Its Application in the BTH Region
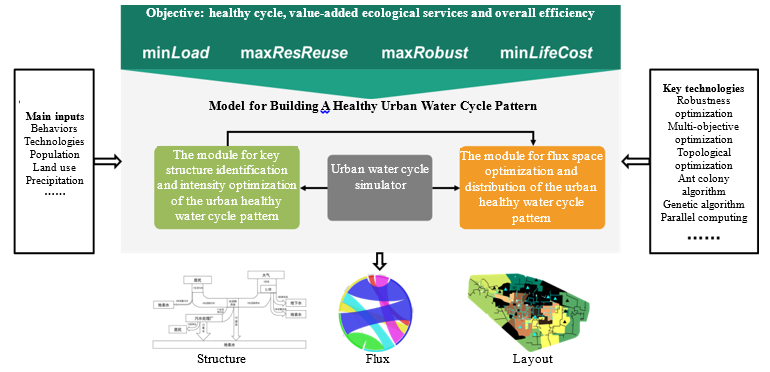
Fig.3 Model for Building A Healthy Urban Water Cycle
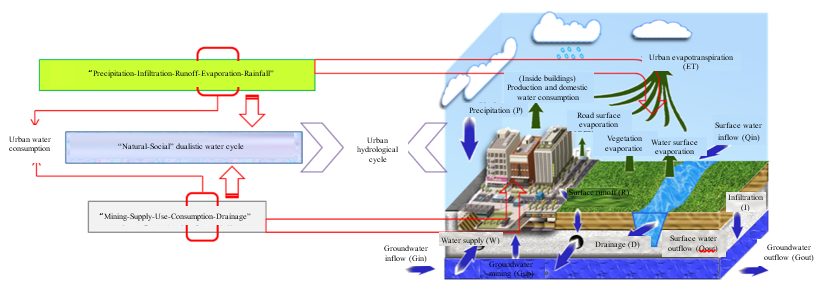
Fig.4 Urban Water Consumption under the Natural-Social dualistic water cycle scenario
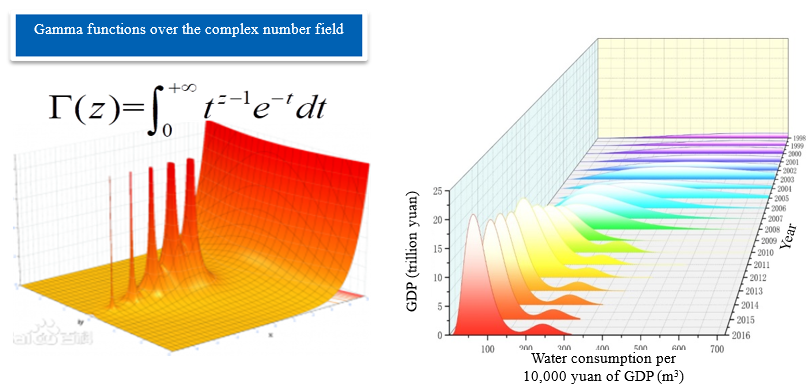
Fig.5 Method for Water Use Efficiency Analysis and Spectral Discretization Based on Gamma Functions
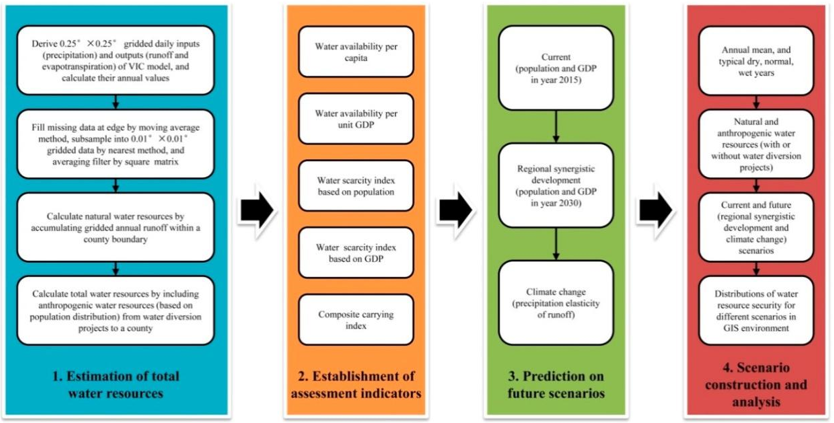
Fig. 6 Method Framework for Water Resources Security Diagnosis in City Clusters