Main Participants: SUN Dongya, GUO Liang, DING Liuqian, KUANG Shangfu, WANG Xiaogang, LIU Changjun, HE Bingshun, LIU Ronghua, LI Qing, ZHAI Xiaoyan, ZHANG Xiaolei, LIU Qi, TIAN Jiyang, SUN Tao, TU Yong, ZHANG Shunfu, LIU Yun, ZHANG Miao, MA Qiang, ZHAO Xueying
Hilly and mountainous areas account for 70% of China’s territory, where flash floods occurrence claims 74% of deaths attributable to floods each year. Flash flood prevention constitutes a weak aspect in flood control and disaster mitigation. Since 2010, China for the first time launched a national flash flood prevention program including the construction of monitoring and early-warning systems at different levels of institutions, with an investment of RMB 11 billion. Compared with that for rivers and lakes, the theoretical and technological foundation of flash flood prevention is quite weak: the temporal and spatial characteristics of the main dominant factors of the storm-flood-disaster chain and their quantification are poorly understood; and the models, methods, techniques or standards for monitoring and warning are almost blank. This project aims to quantitatively address core scientific problems such as uncertainties of flood simulation, monitoring and warning in small catchment in order to improve the accuracy of early-warning, extend the flood forecasting lead time, expand the coverage of warning, and enhance the resilience of the system.
· Constituting
the theoretical and technological system for flash flood monitoring and early-warning
in China;
· Studying
the characteristics and patterns of storms in hilly and mountainous regions and
runoff generation and confluence at small catchment scale, as well as the
characteristics of flash flood events;
· Developing
a non-linear runoff generation and concentration simulation technology for
small catchment in case of a flash flood, and software products of hydrological
simulation systems for flash floods in small catchments;
· Establishing
techniques and methods for early-warning of flash floods in small catchments,
and developing methods for identifying the risk of flash floods at small catchment
scale and analyzing warning thresholds;
· Establishing
systematic flash flood monitoring and warning standards.
· A system of theories and technologies for flash flood monitoring and warning in China is established, the overall layout of the national flash flood monitoring and warning system is proposed, a multi-stage progressive forecasting and early-warning model for flash floods is created, and methods for simulating flash floods in small catchments and analyzing dynamic critical rainfall and warning threshold are developed.
· The characteristics and temporal and spatial distribution of disaster-causing storms in China are revealed, the hydrological characteristics of small catchments and spatial heterogeneity of underlying surfaces conditions across the country are identified, and the temporal and spatial distribution patterns, classification and causes of flash floods are ascertained.
· A dynamic flash flood forecasting and early-warning system is established coupling the factors of “hydrology, meteorology and risk”, and the threshold calculation methods for dynamic warning in different stages and methods for analyzing key parameters such as soil moisture are developed. A non-linear flash flood simulation method for small catchments is proposed, and a proprietary software, namely China National Flash Flood Hydrological Model (CNFF), is developed.
· A dynamic integration technology and parallel computing system for heterogeneous models in the state monitoring and warning platform is developed, an total-factor information correlation model for flash floods is proposed, and the technical framework of provincial cloud platform of monitoring, forecasting and warning is established which allows deployment at provincial level and application at multi-levels of institutions.
· Systematic flash flood monitoring and early-warning standards are established for the first time, blazing a mature technical route. The methods and techniques are developed and constantly improved for determining the early-warning thresholds, building the architecture of monitoring and warning platform, and achieving community-based monitoring and preparedness. Based on this project, four specifications and 28 guidelines are set up.
The research achievements have underpinned the implementation of major national strategies including disaster prevention, poverty alleviation and rural revitalization, and have been applied in the establishment of flash flood monitoring and early-warning systems of the Ministry of Water Resources, the Ministry of Emergency Management, China Meteorological Administration, seven river basin authorities, 29 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, 305 prefecture-level cities and 2,076 counties. For five consecutive years, risk warnings of flash floods have been released on CCTV during prime hours. These work have brought about significant disaster prevention benefits and reducing casualties by over 70%. Meanwhile, the research achievements have also been extended to services such as storm flood warnings for check dams on the Loess Plateau and national natural disaster risk survey program, bringing about noticeable socio-economic benefits.
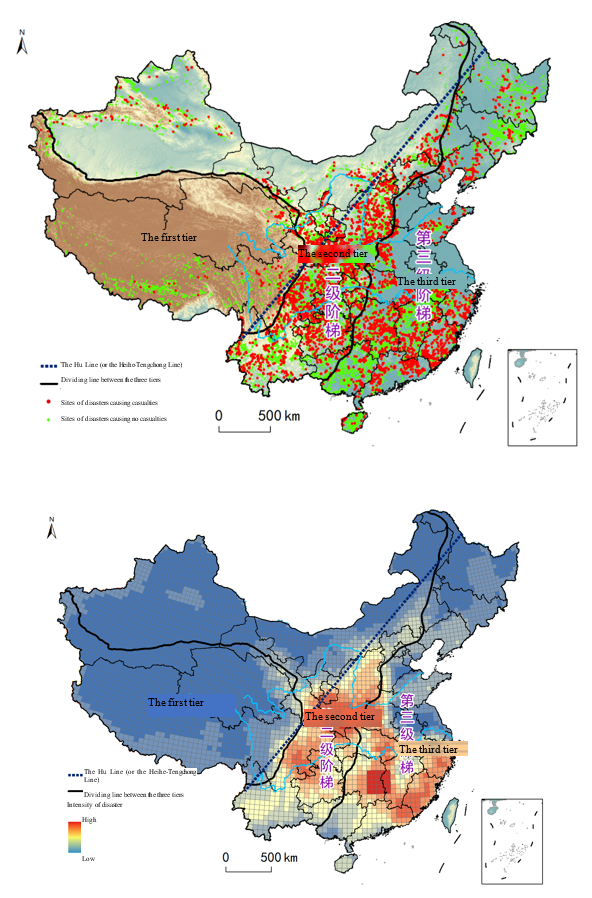
Fig.1 Distribution of Flash Floods in China
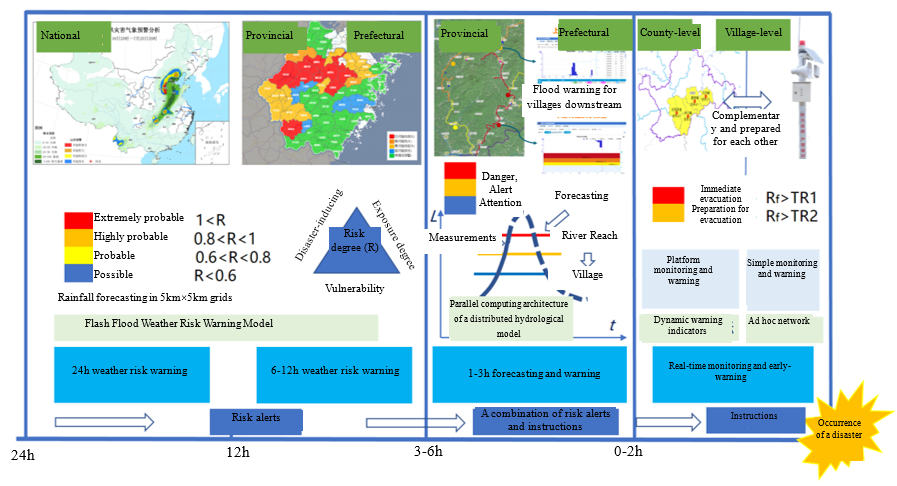
Fig.2 Multi-stage Progressive Flash Flood Forecasting and Early-Warning System
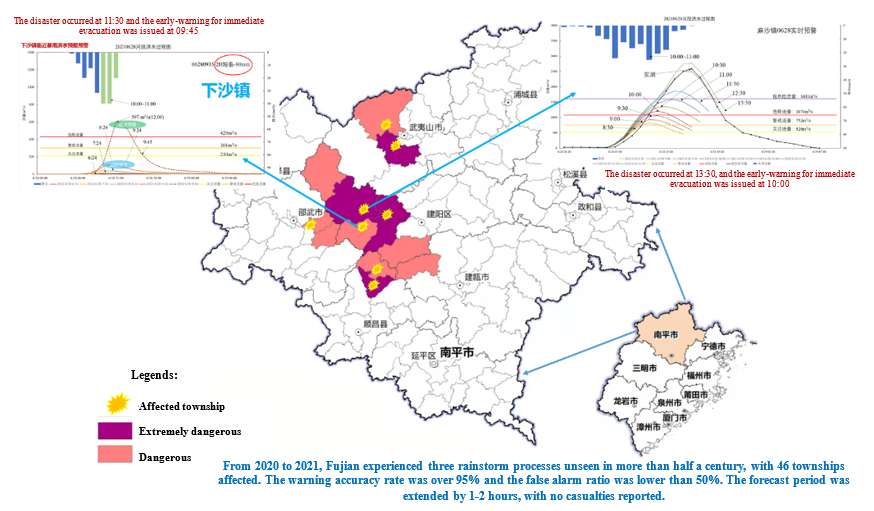
Fig.3 Application of Multi-stage Progressive Forecasting and Early-Warning (with the accuracy rate increased and extended forecasting lead time)
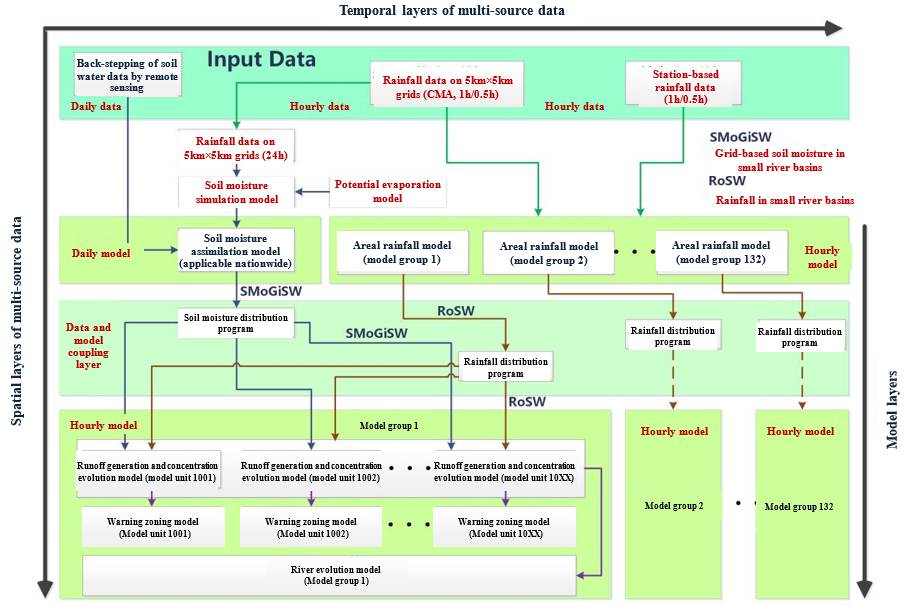
Fig.4 CNFF Layering and Coupling Framework
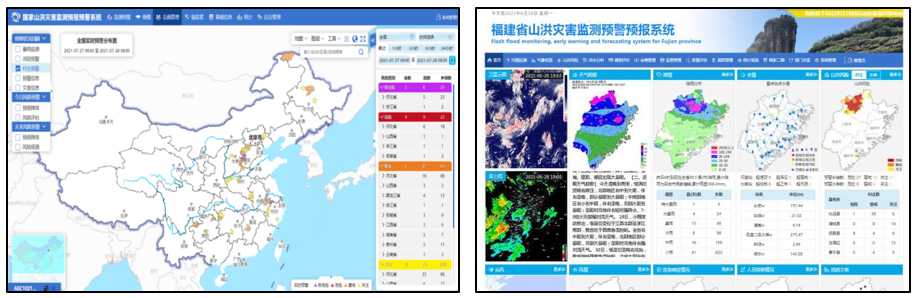
a. National Flash Flood Monitoring, Forecasting and Early-Warning System
b. The Flash Flood Monitoring, Forecasting and Early-Warning System for Fujian Province
Fig.5 Flash Flood Monitoring, Forecasting and Early-Warning Systems