Main Participants: ZHAO Yong, ZHAI Jiaqi, WANG Qingming, REN Changjiang, GONG Jiaguo, HE Guohua, LIU Rong, MA Mengyang, HAN Jingyan, DIAO Weijie, YANG Miao, LI Enchong, GUI Yunpeng, WANG Yong, CHANG Huanyu
In the past 60 years, the water resources in Haihe River Basin have declined sharply, which has caused serious water supply crisis and ecological and environmental problems. Where has the water gone? What is the reason for these changes? How will it evolve in the future? These problems are world-class scientific challenges and edge cutting research topics, bearing a profound impact on the water security and major project planning of the river basin. With the long-term support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and major public welfare projects, the evolution mechanism of water cycle and the attributions of water resources attenuation in Haihe River Basin have been presented in a systematic approach, providing key support for water resources evaluation and the treatment of groundwater overexploitation in this river basin.
· Focusing on the key problem of soil moisture migration mechanism in thick vadose zone and based on in-situ observation and systematic simulation, this research has discovered the characteristics of zero water flux, proposed the three-layer variation laws of evaporation infiltration alternate change, unstable infiltration and relative stable infiltration in thick vadose zone, found the hysteresis and regulation effect of thick vadose zone, put forward the quantitative relationship between mean pore velocity and wetting front velocity, constructed the recharge coefficient of precipitation infiltration under different conditions in Haihe River Plain, identified the real reduction volume of groundwater abstraction with different irrigation efficiencies, and proposed the variation laws of groundwater attenuation in Haihe River Plain.
· Focusing on the new phenomenon that soil water repellency is enhanced in Haihe River Basin because of organic matter increase in the soil as a result of vegetation restoration, and based on extensive investigation, systematic experiment and artificial precipitation simulation, this research has revealed the soil water repellency characteristics and infiltration mechanism, discovered the five-stage precipitation infiltration characteristics of water repellent soil, obtained the reasons for the cumulative infiltration mutations and the change of single peak curve of infiltration rate and established a unified precipitation infiltration model for hydrophilic and water repellent soil to solve the problem of discontinuous inflection point of infiltration rate of hydrophobic soil and realize the mutual conversion with traditional infiltration models such as Horton.
· Focusing on the new problem that land subsidence significantly changes groundwater circulation parameters and water storage capacity, this research has put forward for the first time the nonlinear compressed water release numerical simulation method based on the time-series satellite interferometric radar (InSAR) evaluation, breaking through the barrier that GRACE satellite cannot separate the unrecoverable part of the deep groundwater reserves change, realizing the systematic evaluation of the influence of land subsidence on hydrogeological parameters, and reveal the law of irreversible inelastic water release coefficient and permanent loss of water storage capacity caused by large-scale land subsidence.
· Having analyzed item by item the formation and evolution mechanism of water resources such as precipitation, evaporation, vegetation restoration, water body, groundwater table and farmland tillage, simulated and evaluated the dominant factors and their respective quantitative contributions to water resources attenuation in Haihe River Basin in the past 60 years, independently developed the distributed water cycle simulation model adapted to the influence of strong human activities that realizes the systematic simulation of the dynamic transformation relationship of 12 representative human activities and 60 water cycle elements, predicts the amount of water resources in the basin under different changing conditions such as future climate, underlying surface, vegetation and groundwater table, and predicts the evolution trend of water resources in the future.
After 12 years of research, 105 papers including 52 SCI and 14 EI papers and two monographs have been published; 35 patents and 16 software copyrights have been obtained; three pieces of important advices have been approved by the leaders of the Party and the State, systematically supporting the practice of water resources evaluation and the reverse of groundwater overexploitation in Haihe River Basin.
|
|
|
Fig. 1 Soil Moisture Observation and Migration Law in Thick Vadose Zone
|
|
|
Fig. 2 Rain-runoff Observation and Five-stage Infiltration Law of Water Repellent Soil
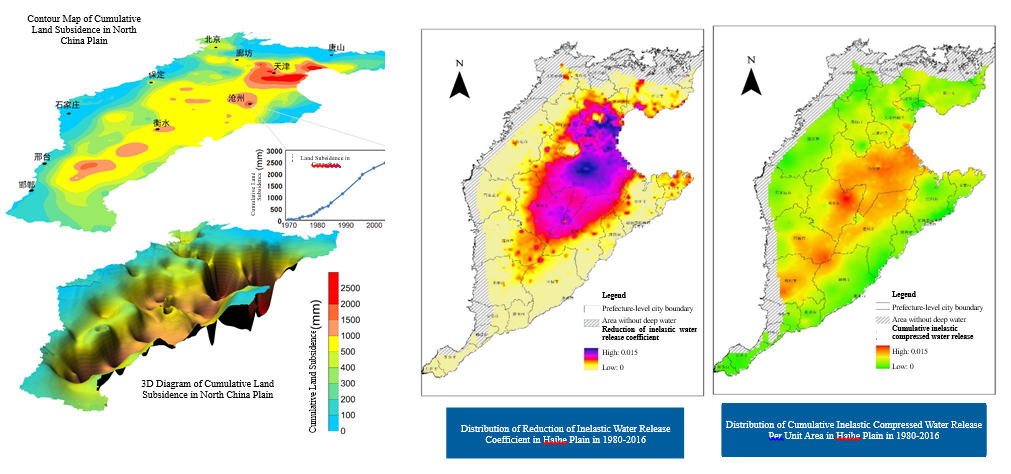
Fig. 3 Water Release Coefficient and Reserves Change of Deep Groundwater in Haihe River Plain